Electric rays: the "Pikachu" and "generator" of the ocean
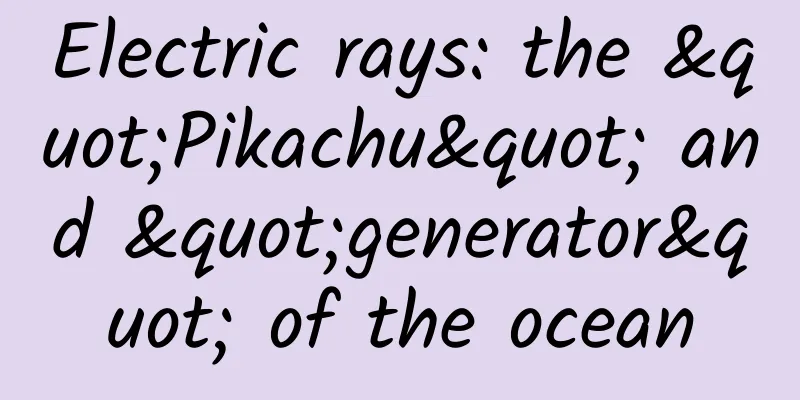
|
Electric rays are cartilaginous fish belonging to the order Gnaphalidae, which has three families: Gnaphalidae, Gnaphalidae and Gnaphalidae. They are characterized by a pair of electric organs on their head and chest, which can release powerful electric currents for defense and hunting. They are fan-shaped, flat on the back and abdomen, with a round or oval head and a thick stick-shaped tail. They have small eyes, a small or medium-sized mouth, and small and numerous teeth. Their skin is smooth and scaleless, mostly gray-brown or reddish-brown in color, sometimes with irregular dark spots. Electric rays are mainly distributed in the coastal waters of tropical and temperate zones around the world. They are commonly found in shallow waters, and a few deep-sea electric rays can live in waters as deep as 1,000 meters. They are bottom-dwelling fish that move slowly and feed on fish and invertebrates. They are ovoviviparous and give birth to a small number of offspring each time. 1. How do electric rays discharge electricity? The electric rays' power generating organs are made up of modified muscle tissue and are located on both sides of the ventral surface of the head and thorax. Each power generating organ is composed of many hexagonal "electric plates", each of which is equivalent to a small battery with positive and negative poles. The surface of each "electric plate" is distributed with nerve endings that can receive signals from nerve pulses. When the electric ray wants to discharge, it sends nerve pulses through the central nervous system, causing a potential difference between the "electric plates" and releasing current. These currents flow from the positive pole to the negative pole, that is, from the back to the ventral surface, forming a strong electric field in the water. Different types of electric rays have different voltages and intensities. Generally speaking, large electric rays have higher voltages, which can reach 200 volts or even higher. Small electric rays have lower voltages, which are only a few dozen volts. But even small electric rays should not be underestimated, because they can release multiple pulses of current in rapid succession. This can have a cumulative effect, causing greater damage to prey or enemies. 2. Why do electric rays discharge electricity? Electric rays discharge electricity for two main purposes: defense and hunting. In terms of defense, electric rays are vulnerable to attacks from other predators in the ocean due to their large size and slow movements. Therefore, electric rays use discharge to protect themselves. When they sense danger, they release a strong electric current to the surrounding area, causing the enemy to retreat or faint due to the electric shock. The electric rays' discharge ability makes them almost without natural enemies in the ocean, and only some large sharks or dolphins dare to compete with them. In terms of predation, since electric rays have small eyes and poor vision, they mainly rely on inductance to detect prey around them in the water. There is a weak electric field around the electric ray's body. When other animals approach, it will interfere with this electric field, allowing the electric ray to detect the location and size of the prey. Then, the electric ray will send one or more strong electric currents to the prey, paralyzing or killing the prey, and then swallow it with its mouth. The electric ray's ability to discharge electricity allows them to prey on animals of various sizes, including fish, crustaceans, mollusks, sea snakes, turtles, etc. 3. What impact do electric rays have on humans? Electric rays have two main impacts on humans: harm and utilization. In terms of hazards, since the electric current released by electric rays is very strong, if humans accidentally touch them or irritate them, they will suffer serious electric shock injuries. This injury may cause muscle spasms, breathing difficulties, heartbeat disorders, nerve paralysis, coma and even death. Therefore, when diving or fishing, try to avoid contact with electric rays. If unfortunately you are electrocuted, you must promptly provide first aid and seek medical treatment. In terms of utilization, since electric rays have the characteristic of discharging electricity, humans can get some inspiration and reference from them. For example, humans invented batteries that can store electricity, which was inspired by the gel in the electric ray generator. In addition, in medicine, humans also use the weak pulse currents emitted by electric rays to treat some diseases of the nervous system or muscle system. These all show that humans can learn and innovate from nature. |
<<: Are the facial masks we use every day useful? Are they just a waste of money?
Recommend
Should you eat first or brush your teeth first when you wake up in the morning? This is actually a big question!
What is the first thing to do when you wake up in...
Water droplets "walking" on oil film, this is not science fiction! The secret of water droplets "dancing"
Your browser does not support the video tag Autho...
The efficacy and function of rabbit bones
The essence of traditional Chinese medicine is to...
If Darwin were alive today, he would rethink "The Origin of Species"
Anyone who has seen the movie "Prometheus&qu...
National Defense Science Popularization Gas Station (36) Supercontinuum Laser: An Extraordinary New Light Source
In the field of optics, laser has the characteris...
The efficacy and function of goose bile
Goose bile is a kind of traditional Chinese medic...
The efficacy and function of jackfruit leaves
Jackfruit leaves are a kind of traditional Chines...
The efficacy and function of Yunnan Tibetan cypress
Yunnan-Tibetan cypress is a very good medicinal m...
Evidence of Beijing's 3,000-year history is here! A picture shows the new archaeological achievements of the Liulihe site
The Beijing Municipal Cultural Heritage Bureau an...
Chinese herbal medicine for sterilization and anti-inflammatory
There are many types of Chinese medicinal materia...
What are the medicinal values of roselle?
What is Roselle? Most northerners may not know th...
The efficacy and function of daughter red root
Nv'erhong root is a traditional Chinese medic...
The efficacy and function of the root of stinking grass
Modern medical research believes that the roots o...
What are the medicinal values of Bupleurum?
Bupleurum is a very common Chinese medicinal mate...




![The efficacy and function of Gexianmi [picture]](/upload/images/67ca717e093d0.webp)




